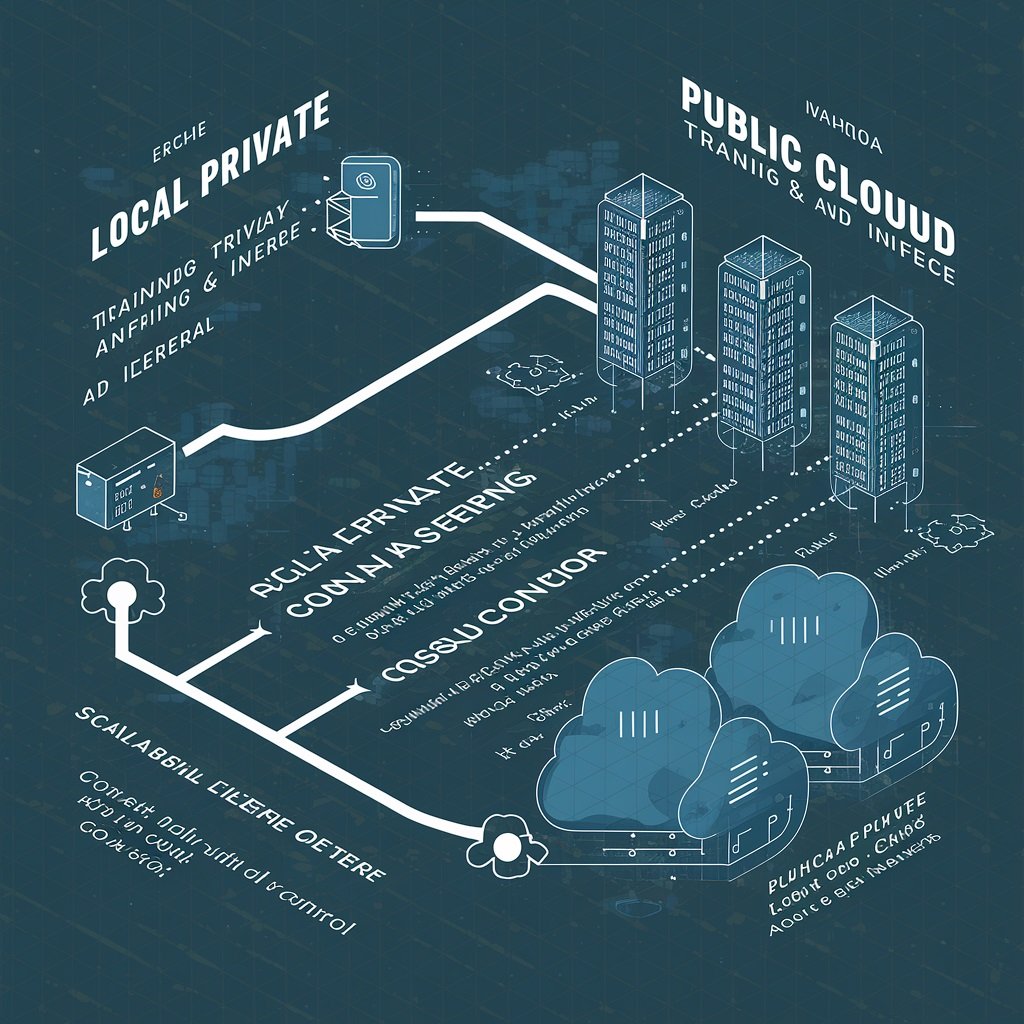
Private vs. Public AI Servers: Navigating the Landscape
In the ever-evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI), organizations face critical decisions when it comes to deploying and managing AI models. One of the fundamental choices is whether to opt for private, local AI servers or rely on traditional public, cloud-hosted AI services. In this article, we delve into the implications and benefits of each approach, considering factors such as data privacy, security, and performance.
1. Data Privacy and Control
Private, Local AI Servers
- Data Sovereignty: Organizations that deal with sensitive data—such as healthcare records, financial transactions, or proprietary research—often require strict control over their data. Private AI servers allow companies to keep their data within their own infrastructure, ensuring compliance with regulations and minimizing exposure to external risks.
- Customization: Local servers provide the flexibility to customize AI environments according to specific business needs. Whether it’s fine-tuning hyperparameters or integrating specialized hardware, organizations have greater control over their AI stack.
- Isolated Environments: By keeping AI training and inference within the organization’s premises, companies can create isolated environments that reduce the risk of data leaks or unauthorized access.
Public, Cloud-Hosted AI Servers
- Convenience and Scalability: Public cloud services offer convenience and scalability. Organizations can quickly spin up AI instances, scale resources as needed, and leverage pre-built services. This agility is especially valuable during development and prototyping.
- Shared Responsibility: While cloud providers invest heavily in security, the responsibility for data protection is shared. Organizations must trust the provider’s security measures and adhere to best practices. However, this shared responsibility can be a double-edged sword, especially in regulated industries.
- Global Accessibility: Cloud services provide global accessibility, enabling seamless collaboration across geographies. Teams can work together on AI projects without worrying about physical infrastructure limitations.
2. Data Security and Compliance
Private, Local AI Servers
- Regulated Industries: Sectors like healthcare (HIPAA), finance (FINRA), and government (FISMA) demand rigorous data security. Local servers allow organizations to implement industry-specific security protocols, audit logs, and encryption standards.
- Air Gap Possibility: Some organizations opt for air-gapped AI servers, physically isolating them from external networks. While this enhances security, it also limits connectivity and updates.
- Reduced Attack Surface: By minimizing exposure to the internet, private servers reduce the attack surface. However, organizations must still address internal threats.
Public, Cloud-Hosted AI Servers
- Certifications and Compliance: Leading cloud providers comply with industry standards and certifications. However, organizations must verify that their chosen provider aligns with their specific regulatory requirements.
- Shared Infrastructure: Cloud services share infrastructure across multiple clients. While this optimizes resource utilization, it introduces potential risks. A breach affecting one client could indirectly impact others.
- Encryption and Access Controls: Cloud providers offer robust encryption and access controls. Organizations can configure fine-grained permissions, but misconfigurations remain a concern.
3. Performance and Resource Allocation
Private, Local AI Servers
- Resource Exclusivity: Perhaps the most significant advantage of local servers is resource exclusivity. Organizations don’t compete with a global audience for compute power, resulting in consistent performance.
- Latency and Throughput: In latency-sensitive applications (e.g., real-time predictions), local servers excel due to reduced network hops.
- Cost Predictability: Local infrastructure costs are predictable, avoiding unexpected billing spikes.
Public, Cloud-Hosted AI Servers
- Elasticity: Cloud services allow dynamic resource allocation. However, noisy neighbors (other users on the same hardware) can impact performance.
- Cost Variability: While cloud services offer flexibility, costs can fluctuate based on usage patterns.
- Global Reach: Cloud providers have data centers worldwide, enabling low-latency access for users across regions.
Choosing between private and public AI servers involves trade-offs. Organizations must evaluate their specific needs, regulatory requirements, and long-term goals. For mission-critical applications, private servers offer control and security, while cloud services provide agility and scalability. Ultimately, the decision hinges on striking the right balance between privacy, security, and performance in an AI-driven world.









Leave a Reply